Fundus examination
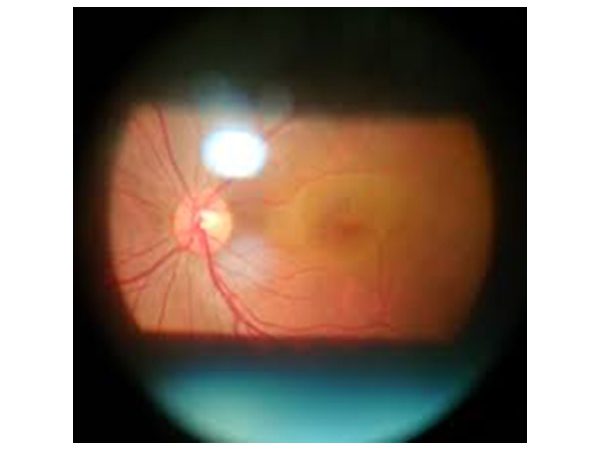
Funduscopy or Ophthalmoscopy or Retinal examination is a test that allows your ophthalmologist to look at the back of your eye. This part of your eye is called the fundus, and consists of Retina, Optic disc and Blood vessels
This test is often included in a routine eye exam to screen for eye diseases esp. if you have a condition that affects your blood vessels, such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Dilated fundus examination is a diagnostic procedure that employs the use of mydriatic eye drops (such as tropicamide) to dilate or enlarge the pupil in order to obtain a better view of the fundus of the eye. Once the pupil is dilated, examiner uses indirect ophthalmoscope to view the eye's interior, allowing assessment of the Retina, Optic disc and Blood vessels, and other features of retinal periphery. Dilated Fundus Examination has been found to be a more effective method for evaluation of internal ocular health than non-dilated examination
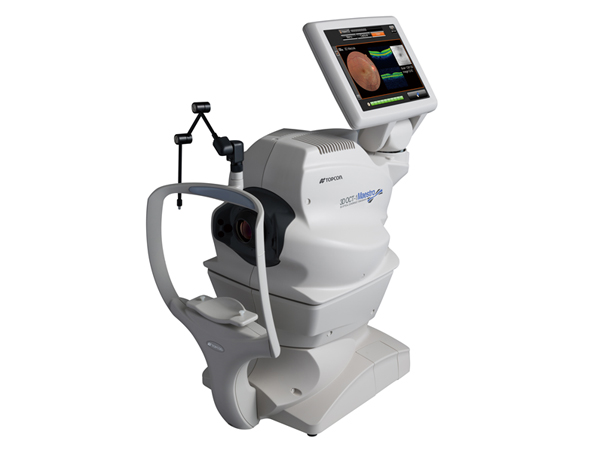
Fundus camera is used to keep a photographic record of fundus for future reference
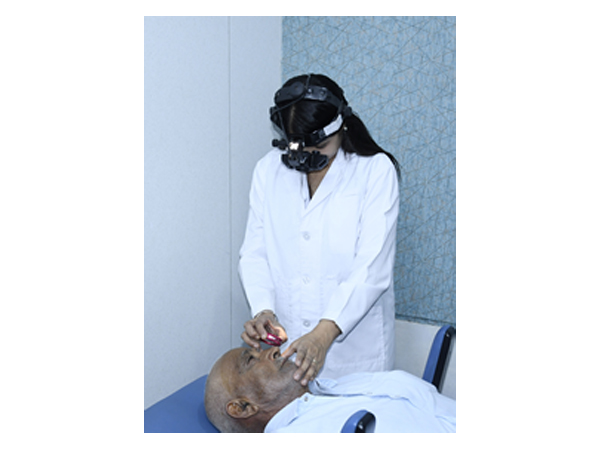
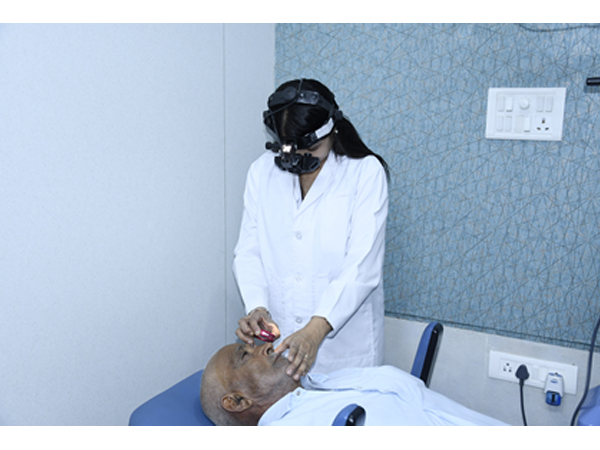
Indirect Ophthalmoscopy
An indirect ophthalmoscope constitutes a light attached to a headband, in addition to a small handheld lens. It provides a wider view of the inside of the eye. Furthermore, it allows a better view of the fundus of the eye even if the lens is clouded by cataracts. It is used for peripheral viewing of the retina.
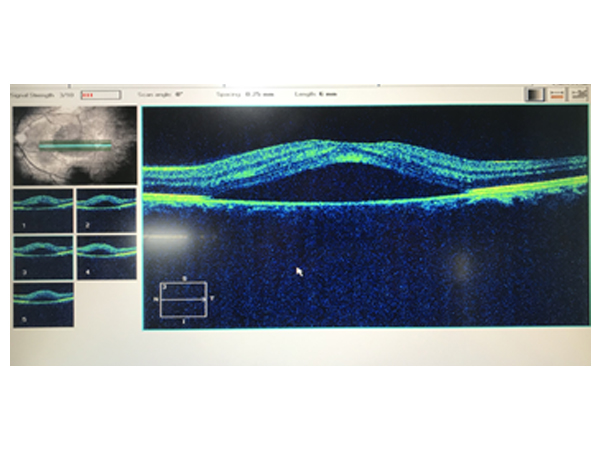
OCT
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test. OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your eye structures like Cornea, Anterior segment, Retina and Optic Nerve. With OCT, your ophthalmologist can see of the distinctive layers of the different structures. This allows to map and measure their thickness. It has revolutionised the diagnosis of various ocular disorders. It has different modes to help in assessing and henceforth assisting in deciding treatment protocols as well as monitoring progress.
OCT for Retina
It has become the backbone of Retinal disorder diagnosis and management. Common Retinal disorders whose management has improved immensely by the assistance of OCT are:
Diabetic Retinopathy
Age Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD)
Retinal Vascular Disorders like CRVO, BRVO
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy or CSR
Uveitic Macular Edema
Assessment of Structural changes in Drug (Medication) Induced Retinopathy
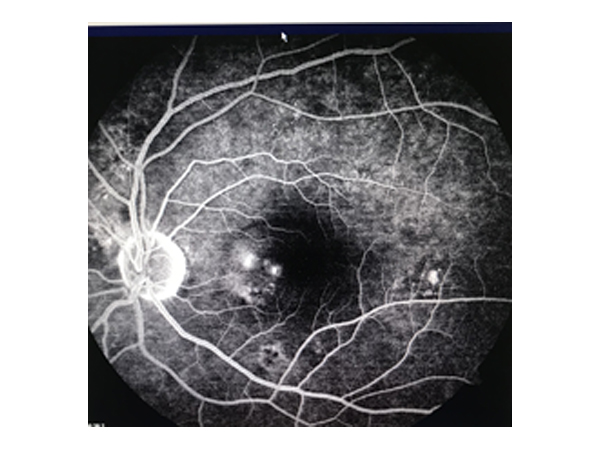
FFA
A fluorescein angiography is a medical procedure in which a fluorescent dye is injected into the bloodstream. The dye highlights the blood vessels in the retina of the eye so they can be photographed. This test is often used in diagnosis and management of posterior segment disorders including diabetic retinopathy.
This is an invasive test with a very rare possibility of allergy to fluorescein dye.
Nausea and discoloration of urine is common
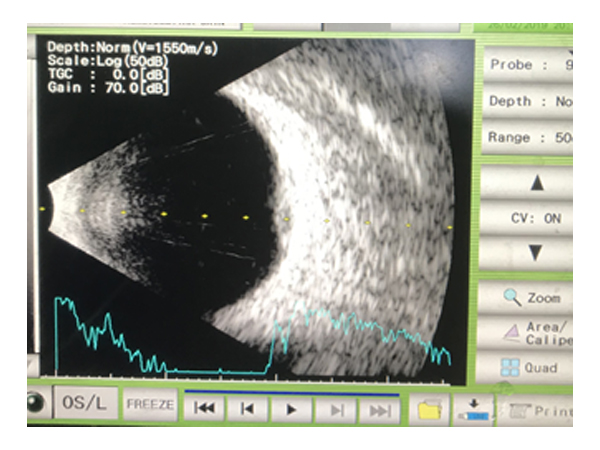
B Scan
B scan Ultrasonography, often called just B scan
It offers two-dimensional cross-sectional view of the eye as well as the orbit. A B scan is used on the outside of the closed eyelid to view the eye. This type of diagnostic tool is most helpful when there is difficulty examining the posterior segment normally.
It helps in
Closed globe Trauma assessment
Intra-ocular bleeding
Retinal Detachment
Ocular and orbital Tumours
Orbital and intraocular Foreign body assessment
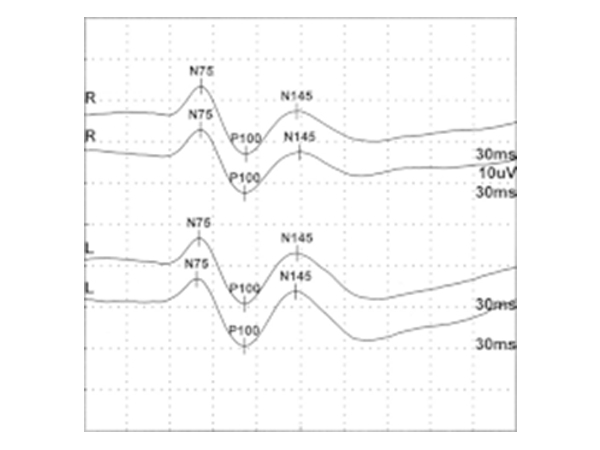
VEP and ERG
VEP is an acronym for Visual Evoked Potential. This is a test to determine the integrity of the nerve transmission from the eye to the brain. Electrode receptors are attached to the back of the head and various light stimuli are presented to the eyes and the response is monitored.
Electroretinography (ERG) is an eye test that detects function of the retina (the light-detecting portion of the eye). The retina is comprised of layers of specialized cells, including photoreceptors (rods and cones), that detect light and ganglion cells that transmit images to the brain.